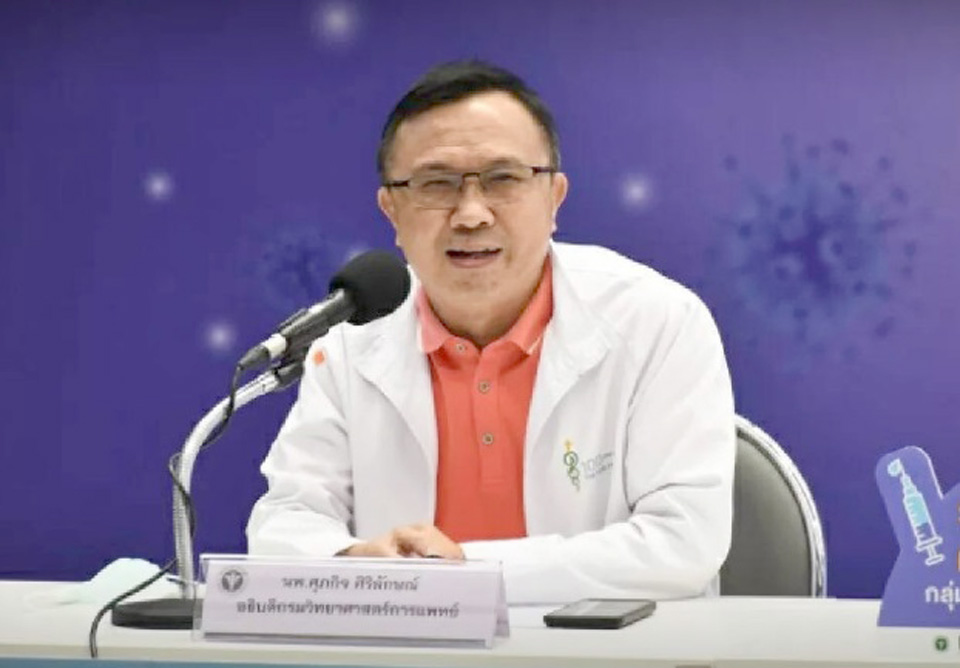
Thailand’s Department of Medical Sciences (DMS) has noted that research shows an intradermal (ID) delivery of the COVID-19 vaccine achieves the same result as traditional intramuscular (IM) vaccination.
DMS Director-General Dr. Supphakit Siriluck said the department divided 95 candidates aged 18 to 60, who had received two Sinovac jabs, into three groups for the study. The first group of 30 received one full dose [0.5ml] of the AstraZeneca vaccine using the IM method. The second group of 31 received a fifth [0.1ml] of the AstraZeneca jab via the ID method four to eight weeks after they received their second shot of Sinovac. The rest of the participants also received a fifth of the AstraZeneca dose via the ID method, but eight to 12 weeks after their second jab.
He said 14 days after receiving the booster, the first group’s immunity level rose to 1,653AU (arbitrary unit), while that of the second and third groups rose to 1,300.5AU on average. Before receiving the booster, the participants’ average immunity level was 128.7AU.
Dr. Supphakit said, since the ID application requires only a fifth of a normal dose to achieve similar results, it can help to increase the rate of vaccination in areas where supplies are limited. However, more skilled medics are required for the ID approach as the needle has to be angled 10 to 15 degrees and only inserted 1mm under the skin. (NNT)
 |
 |
 |